pH Review and Balancing
What Is pH Balancing and Why It Matters for Humans
Maintaining the right pH balance in your body is essential for overall health and well-being. But what exactly does “pH” mean, and why is it so important?
Understanding pH
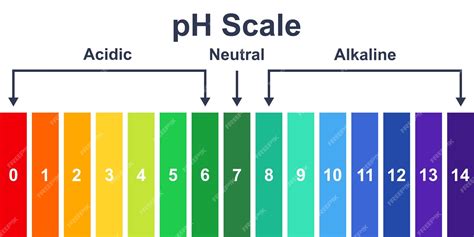
The term pH stands for “potential of hydrogen.” It measures how acidic or alkaline a substance is on a scale from 0 to 14:
- 0–6.9: Acidic
- 7: Neutral
- 7.1–14: Alkaline (or basic)
Your body naturally works to keep its pH within a healthy range. For example, your blood maintains a slightly alkaline pH of about 7.35 to 7.45. Even small changes outside this range can affect how your organs and systems function.
Why pH Balance Is Important
When your body’s pH becomes too acidic or too alkaline, it can disrupt many essential processes. Here’s why keeping your pH balanced matters:
- Supports Healthy Cell Function
Cells thrive in a stable environment. A balanced pH allows enzymes and chemical reactions in your body to work properly. - Boosts Energy and Immunity
An imbalanced pH—especially one that’s too acidic—can lead to fatigue, inflammation, and a weakened immune response. - Protects Bone and Muscle Health
When your body becomes too acidic, it may draw minerals like calcium and magnesium from bones and muscles to restore balance—potentially leading to weakness over time. - Aids Digestion and Detoxification
Proper pH levels in the stomach and intestines help your body break down food efficiently and eliminate toxins.
How to Maintain a Healthy pH Balance
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
- Stay hydrated with clean water.
- Limit acidic triggers like processed foods, soda, and excess caffeine.
- Manage stress, as it can increase acidity in the body.
Consequences of pH Imbalance
- Acidosis: Happens when blood pH drops below 7.35, leading to symptoms like fatigue, confusion, and respiratory issues.
- Alkalosis: Happens when blood pH rises above 7.45, which can cause muscle twitching, hand tremors, and nausea.
